Harnessing the Power of Spaced Repetition
The Leitner System is a scientifically proven method to transition information from your short-term memory to your long-term memory by increasing the intervals between reviews as you master the content.
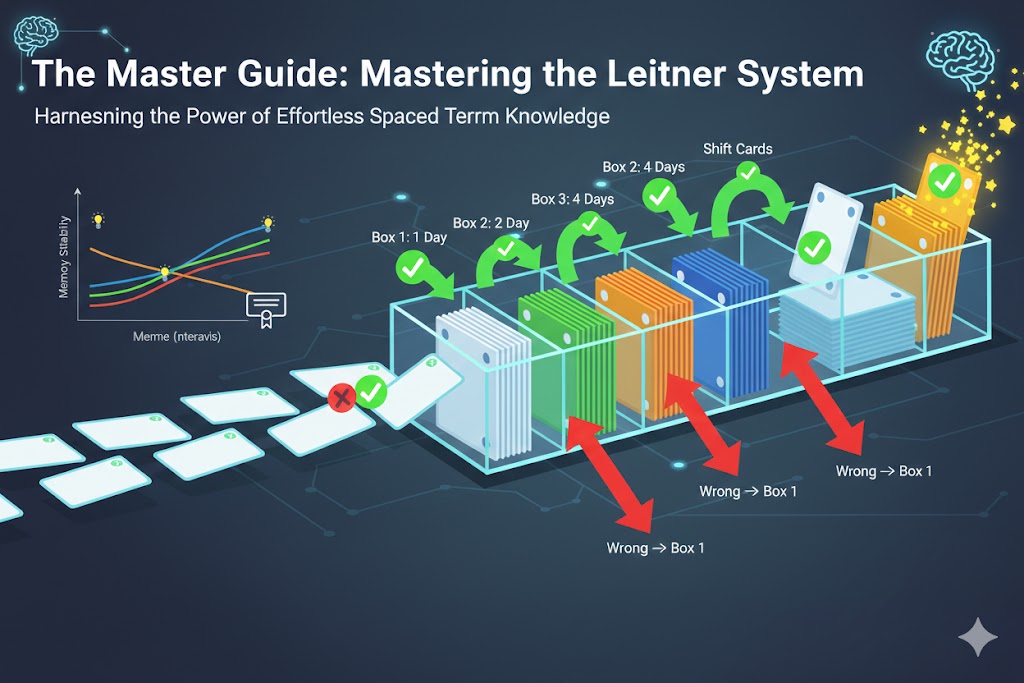
1. The Core Logic: The "Reverse Chain" Rule
To ensure your learning flows without "traffic jams," always work backward from the largest box containing cards toward Box 1. This creates the necessary capacity for cards being promoted from previous boxes.
2. Daily Operational Workflow (The Algorithm)
For each Box (starting from Box 5 down to Box 1), follow these three precise steps:
-
Check the Exit Sub-box: Look at the last sub-box of the current Box. Are there cards waiting?
-
If YES: Test yourself on these cards.
-
Correct Answer: The card is "Promoted" to the first sub-box of the next Box.
-
Wrong Answer: The card is "Demoted" immediately back to Box 1, regardless of its current stage.
-
-
-
The "Shift" (Internal Movement): Once the exit sub-box is processed, shift all remaining cards in the other sub-boxes one unit forward.
-
Capacity Creation: The shift effectively empties the first sub-box of the current Box, making it ready to receive "correct" cards coming from the previous (smaller) Box.
3. Box Structure & Timing
-
Box 1: Every Day (1 sub-box)
-
Box 2: Every 2 Days (2 sub-boxes)
-
Box 3: Every 4 Days (4 sub-boxes)
-
Box 4: Every 8 Days (8 sub-boxes)
-
Box 5: Every 16 Days (16 sub-boxes)
-
Graduation: Once a card passes the 16th sub-box of Box 5 correctly, it is considered Fully Learned and enters your long-term memory.
Every time you correctly recall a card, you are not just "passing a test"—you are physically strengthening the neural pathways in your brain. This is known as Synaptic Plasticity.
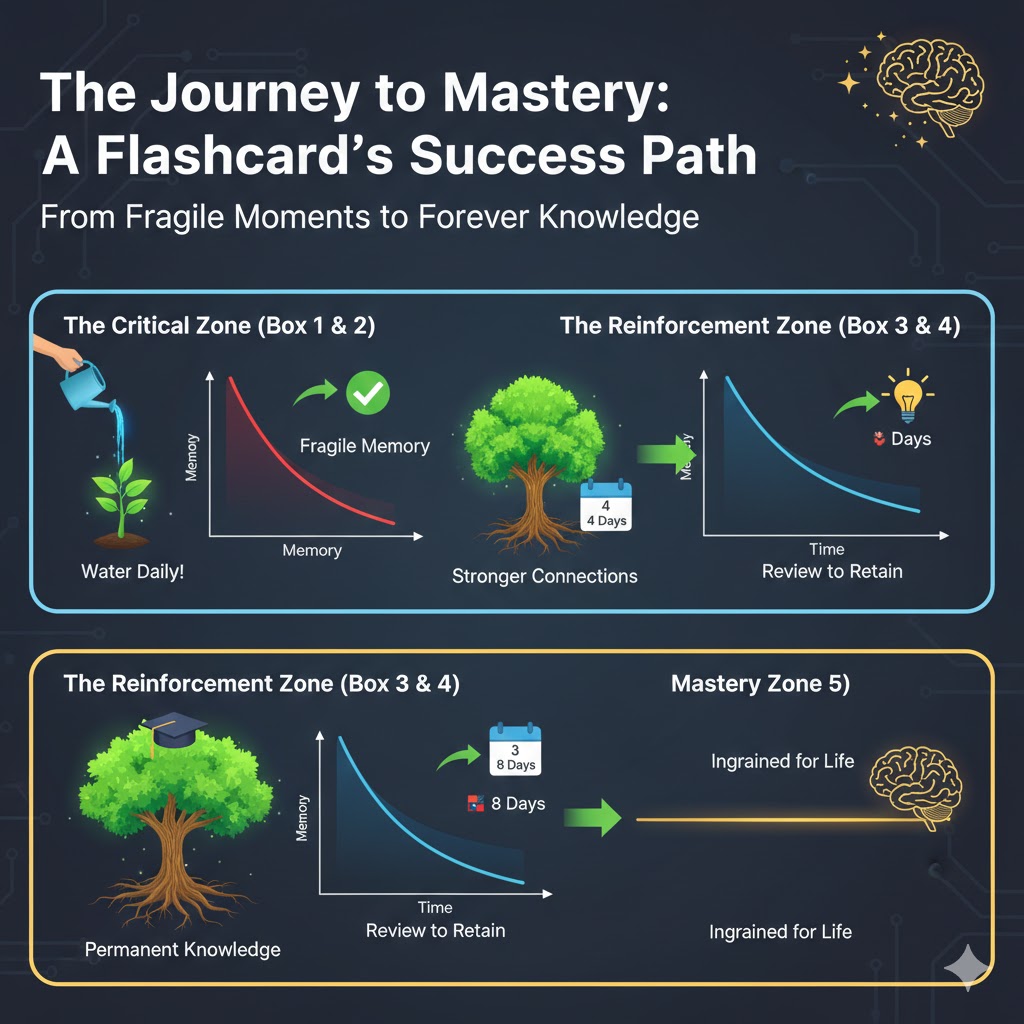
Phase 1: The Critical Zone (Box 1 & 2)
This is where the memory is most fragile. Imagine a memory like a small sapling that needs constant watering to grow.
-
The Struggle: At this stage, the memory is "volatile." Without a review within 24–48 hours, the forgetting curve is extremely steep.
-
The Result: By passing Box 2, you have successfully refreshed and doubled the initial stability of the memory.
-
Retention: You’ve moved from "I just saw this" to "I recognize this."
Phase 2: The Reinforcement Zone (Box 3 & 4)
Here, the intervals grow, and your brain starts to cement the information, making it more robust. Think of this as the sapling growing into a sturdy young tree.
-
The Interval: Now, the gaps between reviews jump to 4 and 8 days. Your brain learns that this information is important enough to be recalled repeatedly over longer periods.
-
The Science: Because you are reviewing the card right as it's about to slip away, the brain marks this information as "High Priority," leading to stronger memory traces.
-
Retention: The forgetting curve starts to flatten significantly. You no longer need to "cram."
Phase 3: The Mastery Zone (Box 5)
This is the ultimate test of long-term retention. Once a card reaches here, it's on its way to becoming ingrained knowledge. Your tree is now mature and deeply rooted.
-
The Endurance: You are now facing the 16-day sub-boxes. To exit Box 5, the card must stay in your head for over two months of cumulative spaced reviews.
-
The Graduation: When the card exits the 16th sub-box of Box 5, the "Forgetting Curve" has become nearly a horizontal line. The information is now practically part of your permanent knowledge base.
-
Retention: Permanent Long-Term Storage.